scala集合
集合简介 Scala的集合有三大类: 序列Seq、集Set、映射Map, 所有的集合都扩展自Iterable特质
对于几乎所有的集合类,Scala都同时提供了可变 和不可变 的版本, 分别位于以下两个包
不可变集合 scala.collection.immutable
可变集合 scala.collection.mutable
scala不可变集合,就是指该集合不可修改,每次修改就会返回一个新对象,而不会对原对象进行修改。类似于Java中的String对象
可变集合,就是这个集合可以直接对原对象进行修改,而不会返回新的对象,类似于Java中的StringBuilder对象
建议:在操作集合的时候,不可变用符号,可变用方法
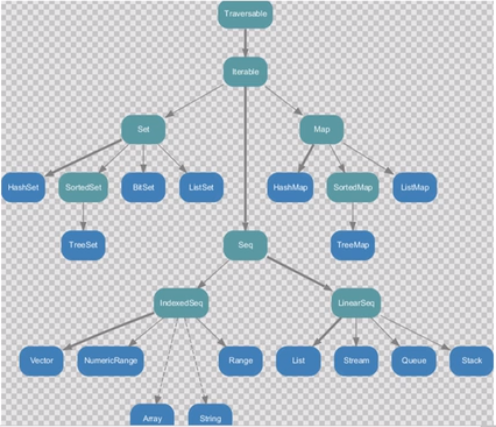
不可变集合继承范围:
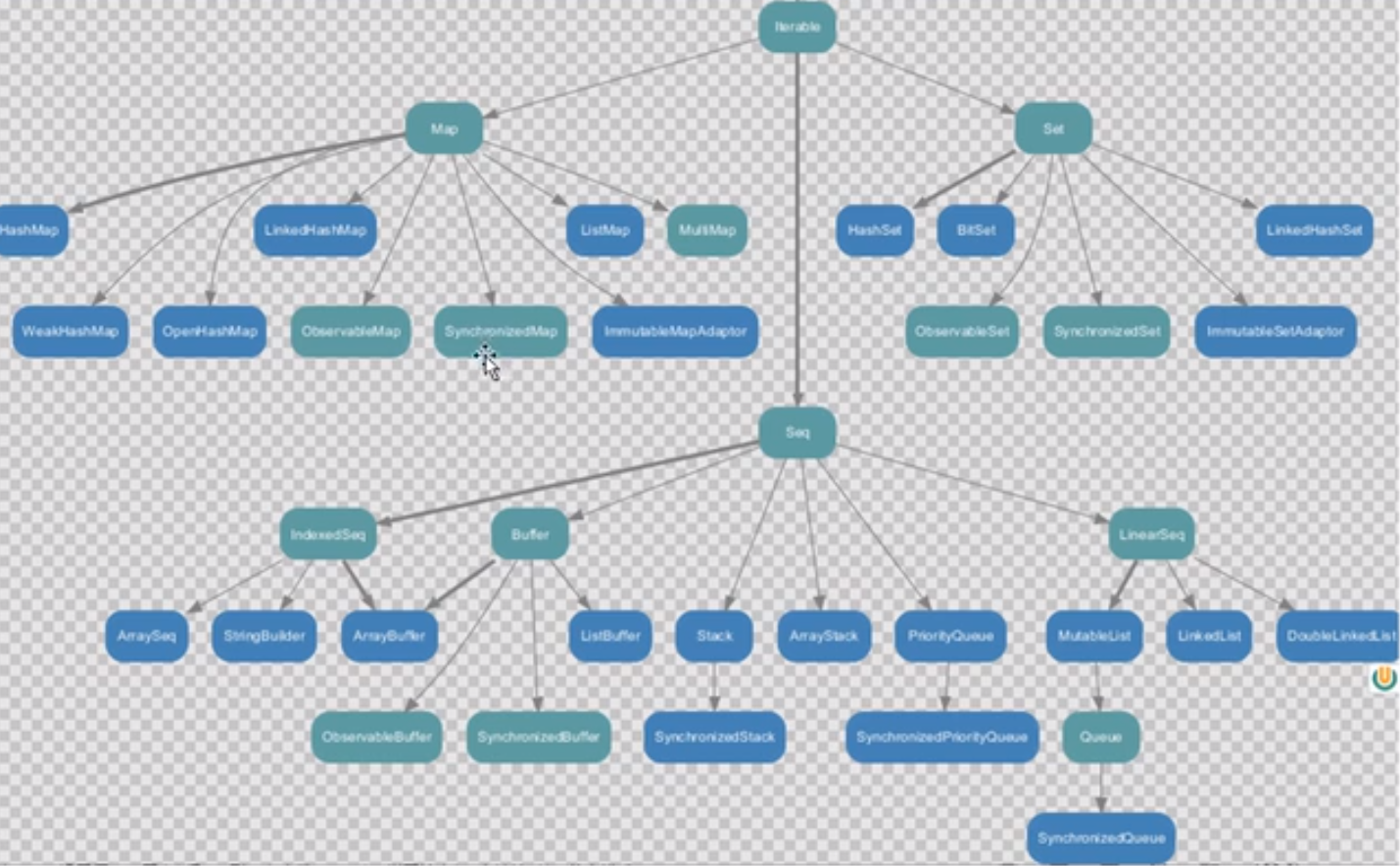
可变集合继承范围
数组 不可变数组 定义: val arr1 = new Array[Int](10)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 object ImmutableArray01 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { val arr: Array[Int] = new Array[Int](5 ) val arr2 = Array(1 ,2 ,3 ) println(arr2(0 )) arr2(0 ) = 77 for (x <- arr2){ println(x) } for (i <- arr2.indices){ println(arr2(i)) } val iter = arr2.iterator while (iter.hasNext){ println(iter.next()) } arr2.foreach( println) println(arr2.mkString("--" )) val newArr = arr2.:+(9 ) println(newArr.mkString("--" )) val newArr2 = arr2.+:(9 ) println(newArr2.mkString("--" )) val newArr3 = arr2 :+ 40 println(newArr3.mkString("--" )) val newArr4 = 40 +: arr2 println(newArr4.mkString("--" )) } }
可变数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 object mutableArrayBuffer02 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { val arr1 = new ArrayBuffer[Int]() val arr2 = ArrayBuffer(1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ) println(arr1.mkString("--" )) println(arr2.mkString("--" )) println(arr2) println(arr2(0 )) val newArr1 = arr2 :+ 9 println(newArr1) arr2 += 9 println(arr2) 77 +=: arr2 println(arr2) arr2.append(31 ) arr2.prepend(22 ) arr2.insert(1 , 32 ) println(arr2) arr2.insertAll(1 ,arr1) println(arr2) arr2.remove(1 ) println(arr2) arr2.remove(1 , 4 ) println(arr2) arr2 -= 9 println(arr2) } }
可变数组和不可变数组转换 1 2 3 val arr2 = ArrayBuffer(1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ) val newArr = arr2.toArray val newArr2 = newArr.toBuffer
二维数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 val array: Array[Array[Int]] = Array.ofDim[Int](2 ,3 ) array(0 )(2 ) = 4 array(1 )(1 ) = 5 for (i <- array.indices; j <- array(i).indices){ print(array(i)(j) + "\t" ) if (j == array(i).length - 1 ){ println() } } array.foreach(_.foreach(println))
List 不可变列表 list 创建、遍历、添加、合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 val list = List(1 ,2 ,3 ) println(list) println(list(1 )) val list2 = list :+ 10 val list3 = 10 +: list println(list2) println(list3) val list4 = list.::(51 ) println(list4) val list5 = Nil.::(18 ) println(list5) val list6 = 17 :: Nil val list7 = 1 :: 4 :: 7 :: 9 :: Nil println(list7) val list8 = list6 :: list7 println(list8) val list9 = list6 ::: list7 println(list9) val list10 = list6 ++ list7 println(list10)
可变列表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 val list1 = new ListBuffer[Int] val list2 = ListBuffer(12 ,34 ,56 ) println(list1) println(list2) list1.append(13 ) list2.prepend(14 ) println(list1) println(list2) list1 += 16 += 25 println(list1) 21 +=: list1 += 77 println(list1) val list3 = list1 ++ list2 println(list3) list1 ++=: list2 println(list1) println(list2) list2(0 ) = 9 println(list2) list2.remove(2 ) list2 -= 77 println(list2)
Set 默认情况下,Scala使用的是不可变set, 如果想使用可变set需要引入 scala.collection.mutable.Set包
不可变集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 val set1 = Set(1 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ) println(set1) val set2 = set1 + 9 println(set2) val set3 = Set(4 ,5 ,6 ) val set4 = set2 ++ set3 println(set4) val set5 = set3 - 5 println(set5)
可变集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 val set1 = mutable.Set(1 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ) println(set1) set1.add(10 ) println(set1) set1.addOne(6 ) println(set1) set1 += 7 println(set1) set1 -= 10 println(set1) set1.remove(7 ) println(set1) val set3 = mutable.Set(4 ,5 ,6 ) val set4 = set1 ++ set3 println(set1) println(set4) set1 ++= set3 println(set3) println(set1)
Map 不可变集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 val map = Map("a" -> 12 , "b" -> 13 ) println(map) map.foreach((kv: (String, Int)) => println(kv)) println(map.get("a" )) println(map.get("a" ).get) println(map.getOrElse("c" , 0 ))
可变集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 val map = mutable.Map("a" -> 12 , "b" -> 13 ) map.put("c" , 6 ) map.put("d" , 9 ) println(map) map += (("e" , 7 )) println(map) map.remove("e" ) println(map) map -= "d" println(map) val map2 = Map("aa" -> 10 , "bb" -> 20 ) map ++= map2 println(map)
元组 元组也是可以理解为一个容器,可以存放各种相同或不同类型的数据,说的简单点,就是将多个无关的数据封装为一个整体,称为元组
注意:元组中最大只能有22个元素
声明方式: (元素2,元素2,元素3)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 val tuple = ("hello" , 100 , 'q' , true ) println(tuple) println(tuple._1) for (elem <- tuple.productIterator){ println(elem) } val mulTuple = (12 ,3 ,5 ,"chen" , (9 ,20 ,"hello" )) println(mulTuple._5._3)
集合常用函数 基本常用操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 val list = List(1 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,8 ) val set = Set(1 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,8 ) println(list.length) println(set.size) println(list.size) for (elem <- list){ println(elem) } set.foreach(println) for (elem <- list.iterator)println(elem) println(list) println(set) println(list.mkString("--" )) println(list.contains(2 ))
衍生集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 val list1 = List(1 ,2 ,4 ,6 ,8 ) val list2 = List(10 ,20 ,40 ,60 ,80 ) println(list1.head) println(list1.tail) println(list1.last) println(list1.init) println(list1.reverse) println(list1.take(3 )) println(list1.takeRight(3 )) println(list1.drop(3 )) println(list1.dropRight(3 )) val union = list1.union(list2) println(union) println(list1 ::: list2) val intersection = list1.intersect(list2) println(intersection) val diff = list1.diff(list2) println(diff) println(list1.zip(list2)) for (elem <- list1.sliding(3 ))print(elem + "\t" )
集合计算简单函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 val list1 = List(5 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,-3 ,8 ) val list2 = List(("a" , 6 ),("b" ,8 ),("c" ,0 ),("d" ,5 )) var sum = 0 for (elem <- list1){ sum += elem } println(sum) println(list1.sum) println(list1.product) println(list1.max) println(list2.max) println(list2.maxBy(_._2)) println(list1.min) println(list1.sorted) println(list1.sorted(Ordering[Int].reverse))
高级计算函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 val list1 = List(1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ) println(list1.filter(_ % 2 == 0 )) println(list1.map(_ * 2 ) ) val nestedList: List[List[Int]] = List(List(1 ,2 ,3 ), List(4 ,5 ), List(6 ,7 )) println(nestedList.flatten) val strings: List[String] = List("hello world" , "hello scala" , "hello java" , "we study" ) val splitList: List[Array[String]] = strings.map(_.split(" " )) val flattenList = splitList.flatten println(flattenList) val flattenList2 = strings.flatMap(_.split(" " )) println(flattenList2) val groupmap = list1.groupBy(_ % 2 ) println(groupmap) val groupmap2 = list1.groupBy(data => if (data % 2 == 0 ) "偶数" else "奇数" ) println(groupmap2) val reduce01 = list1.reduce(_+_) println(reduce01) val list2 = List(3 ,4 ,5 ,8 ,10 ) println(list2.reduce(_ - _)) println(list2.reduceRight(_ - _)) println(list1.fold(10 )(_ + _)) println(list1.foldLeft(10 )(_ - _)) println(list2.foldRight(10 )(_ - _))
归约合并map 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 val map1 = Map("a" -> 1 , "b" -> 2 , "c" -> 3 ) val map2 = mutable.Map("a" -> 6 , "b" -> 4 , "c" -> 7 , "d" -> 1 ) println(map1 ++ map2) val map3 = map1.foldLeft(map2)((mergedMap, kv) => { val key = kv._1 val value = kv._2 mergedMap(key) = mergedMap.getOrElse(key, 0 ) + value mergedMap }) println(map3)
单词计数 经典版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 val stringList: List[String] = List("hello" , "hello world" ,"hello java" ,"hello scala" ,"hello scala from scala" ,"hello flink from scala" ) val worldList = stringList.flatMap(_.split(" " )) println(worldList) val strignToMap = worldList.groupBy(world => world) println(strignToMap) val countMap: Map[String, Int] = strignToMap.map(kv => (kv._1, kv._2.length)) println(countMap) val sortList: List[(String, Int)] = countMap.toList .sortWith(_._2 > _._2) .take(3 ) println(sortList)
复杂版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 val stringList: List[(String, Int)] = List( ("hello" , 1 ), ("hello world" , 2 ), ( "hello java" , 3 ) , ( "hello scala" , 1 ), ("hello scala from scala" , 2 ), ("hello flink from scala" , 3 )) val preCountList: List[(String, Int)] = stringList.flatMap(kv => { val strArr = kv._1.split(" " ) strArr.map(world => (world, kv._2)) }) println(preCountList) val recountMap: Map[String, List[(String, Int)]] = preCountList.groupBy(_._1) println(recountMap) val countMap: Map[String, Int] = recountMap.map(kv => { (kv._1, kv._2.map(tuple => tuple._2 ).sum) }) println(countMap) val resultuple = countMap.toList.sortBy(_._2)(Ordering[Int].reverse).take(3 ) println(resultuple )
并行 Scala 2.13之后,并行集合 模块变成了外部库,直接像Scala 2.12那样写并行集合计算代码,IDE会报“Cannot resolve symbol par”
解决方法:maven 项目的pom.xml中手动导入如下依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.scala-lang.modules</groupId> <artifactId>scala-parallel-collections_2.13</artifactId> <version>0.2.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2, 步骤2: 在使用的并行集合的.scala 文件中引入
1 import scala.collection.parallel.CollectionConverters._
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 val result = (1 to 100 ).map( x => Thread.currentThread().getId ) println(result) val result2 = (1 to 100 ).par.map( x => Thread.currentThread().getId ) println(result2)
模式匹配 模式匹配语法中,采用match关键字声明,每个分支采用case关键字进行声明,当需要匹配时,会从第一个case分支开始,如果匹配成功,那么执行对应的逻辑代码,如果匹配不成功,继续执行下一个分支进行判断,如果所有case都不匹配,那么会执行case_分支,类似于Java中的default语句
基本语法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 val x: Int = 5 val y: String = x match { case 1 => "one" case 2 => "two" case _ => "other" } println(y)
模式守卫 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def abs (num: Int) : Int = { num match { case i if i >= 0 => i case i if i < 0 => -i } } println(abs(9 )) println(abs(-9 ))
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 def describeConst (x: Any) : String = x match { case 1 => "Num one" case "hello" => "String hello" case true => "boolean true" case _ => "无匹配" } def descType (x: Any) : String = x match { case i: Int => "int " + i case i: String => "string " + i case i: List[String] => "List " + i case i: Array[Int] => "Array " + i.mkString("," ) case a => "something else" } println(descType(35 )) println(descType("hello" )) println(descType(List("sd" ))) println(descType(List(5 ))) println(descType(Array(4 ))) println(descType(Array("a" )))
数组匹配 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 for (arr <- List( Array(0 ), Array(1 ,0 ), Array(0 ,1 ,0 ), Array(1 ,1 ,0 ), Array(2 ,3 ,7 ,17 ), Array("hello" , 20 , 30 ), )){ val result = arr match { case Array (0 ) "0" case Array (1 ,0 ) "Array(1,0)" case Array (x,y) "Array: " + x + " , " + y case Array (0 , _*) "以0开头的数组" case Array (x, 1 , z) "中间为1的三元素数组" case _ => "something else" } println(result) }
列表匹配 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 for (arr <- List( List(0 ), List(1 ,0 ), List(0 ,1 ,0 ), List(1 ,1 ,0 ), List(2 ,3 ,7 ,17 ), List("hello" , 20 , 30 ), )){ val result = arr match { case List (0 ) "0" case List (1 ,0 ) "Array(1,0)" case List (x,y) "Array: " + x + " , " + y case List (0 , _*) "以0开头的list" case List (x, 1 , z) "中间为1的三元素list" case _ => "something else" } println(result) }
元组匹配 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 for (arr <- List( (0 , 1 ), (1 ,0 ), (0 ,1 ,0 ), (1 ,1 ,0 ), (2 ,3 ,7 ,17 ), ("hello" , 20 , 30 ), )){ val result = arr match { case (1 ,0 ) => "元组(1,0)" case (x,y) => "元组: (x,y)" case (0 , _) => "以0开头的元组" case (x, 1 , z) => "中间为1的三元素元组" case _ => "something else" } println(result) }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 val (x, y) = ( 10 , "hello" ) println(s"x: $x y: $y" ) println(x) val List (first, second, _*) = List(23 ,3 ,45 ,34 ) println(s"$first $second" ) val fir :: sec :: rest = List(23 ,3 ,45 ,34 ) println(s"$fir $sec $rest" ) val list: List[(String, Int)] = List(("a" , 12 ), ("b" , 23 )) for (elem <- list){ println(elem._1 + "___" + elem._2) } for ((word, coutn) <- list){ println(word + "___" + coutn) } for ((word, _) <- list){ println(word + "___" ) } for (("a" , coutn) <- list){ println("___" + coutn) }
对象匹配 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 object Patt02 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { val student = new Student("chen" , 18 ) val result = student match { case Student ("chen" , 18 ) "yes" case _ => "else" } println(result) } } class Student(val name: String , val age: Int) object Student{ def apply ( name: String, age: Int) : Student = new Student( name, age) def unapply (student: Student) : Option[(String, Int) ] = { if (student == null ){ None }else { Some((student.name, student.age)) } } }
样例类方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 object Patt03 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { val student = Student1("chen" , 18 ) val result = student match { case Student1 ("chen" , 18 ) "yes" case _ => "else" } println(result) } } case class Student1 ( name: String , age: Int)
偏函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 val list = List(("a" , 23 ), ("b" , 56 ), ("c" , 90 ), ("d" , 78 )) val list2 = list.map(tuple => (tuple._1, tuple._2 * 2 )) val list3 = list.map(tuple => { tuple match { case (word, count) => (word, count* 2 ) } }) val list4 = list.map{ case (word, count) => (word, count* 2 ) } println(list3)
异常 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 object Catch01 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { try { val a = 10 / 1 }catch { case e: ArithmeticException =>{ println("算数异常" ) } case e: Exception => { println("异常" ) } }finally { println("结束" ) } } }
隐式转换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 object Yin09 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { implicit def convert (n: Int) : MyRichInt = new MyRichInt(n) println(12. myMax(24 )) implicit class MyRichInt2 (val self: Int) { def myMax2 (n: Int) : Int = {if (self > n) self else n} def myMin2 (n: Int) : Int = {if (self < n) self else n} } println(12. myMax2(24 )) implicit val str: String = "chen" def sayhello (implicit name: String ) : Unit = { println(s"hello $name" ) } def sayhello2 (implicit name: String ) : Unit = { println(s"hello $name" ) } sayhello sayhello2 } } class MyRichInt(val self: Int){ def myMax (n: Int) : Int = {if (self > n) self else n} def myMin (n: Int) : Int = {if (self < n) self else n} }
泛型 协变和逆变 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 object Fan01 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { val child: Parent = new Child val childList: MyCollection[SubChild] = new MyCollection[Child] } } class Parent class Child extends Parent class SubChild extends Child class MyCollection[-E]{}
泛型上下限 class PersonList[T <: Person]{} // 泛型上限
class PersonList[T >: Person]{} // 泛型下限
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 object Fan01 { def main (args: Array[String]) : Unit = { def test[A <: Child](a: A): Unit = { println(a.getClass.getName) } test[Child](new Child) test[Child](new SubChild) test[SubChild](new SubChild) } } class Parent class Child extends Parent class SubChild extends Child