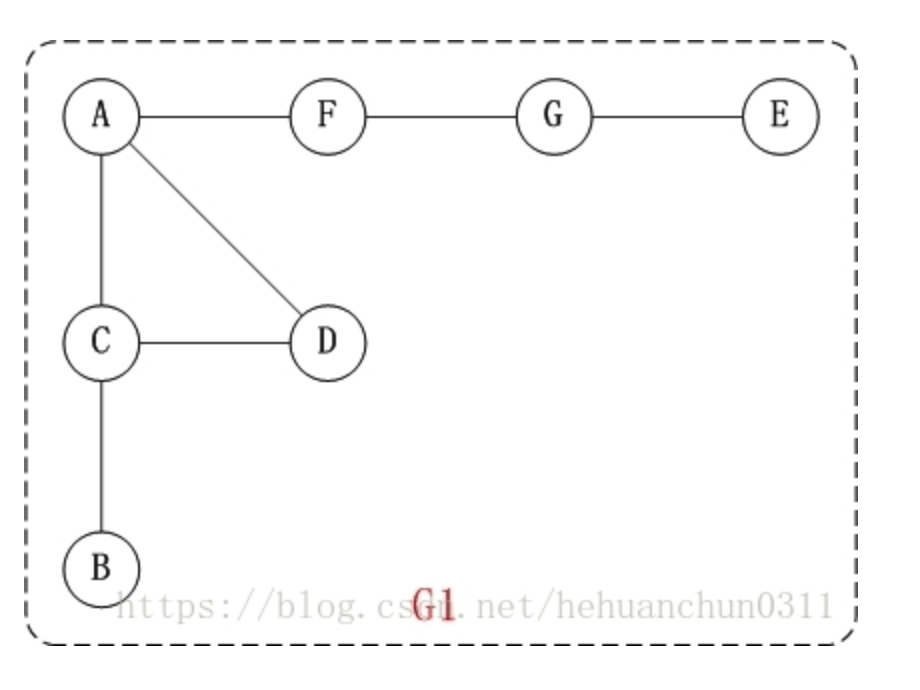
图(Graph)是一种复杂的非线性结构,在图结构中
1 概念 线性表和树两类数据结构,线性表中的元素是“一对一”的关系,树中的元素是“一对多”的关系,本章所述的图结构中的元素则是“多对多”的关系。
图(Graph)是一种复杂的非线性结构,在图结构中,每个元素都可以有零个或多个前驱,也可以有零个或多个后继,也就是说,元素之间的关系是任意的。
无向图: 无向图是由顶点和边构成。
有向图: 有向图是由顶点和有向边构成。
完全图: 如果任意两个顶点之间都存在边叫完全图,有向的边叫有向完全图。如果无重复的边或者顶点到自身的边叫简单图。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class GraphNode <T > T data; List<GraphNode<T>> neighborList; boolean visited; public GraphNode (T data) this .data = data; neighborList = new ArrayList<GraphNode<T>>(); visited = false ; } public boolean equals (GraphNode<T> node) return this .data.equals(node.data); } public void restoreVisited () restoreVisited(this ); } private void restoreVisited (GraphNode<T> node) if (node.visited){ node.visited = false ; } List<GraphNode<T>> neighbors = node.neighborList; for (int i = 0 ; i < neighbors.size(); i++){ restoreVisited(neighbors.get(i)); } } }
2 深度优先和广度优先 2.1 深度优先 1 介绍 图的深度优先搜索(Depth First Search),和树的先序遍历比较类似。
思路:假设初始状态是图中所有顶点均未被访问,则从某个顶点v出发,首先访问该顶点,然后依次从它的各个未被访问的邻接点出发深度优先搜索遍历图,直至图中所有和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。 若此时尚有其他顶点未被访问到,则另选一个未被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。显然,深度优先搜索是一个递归的过程。
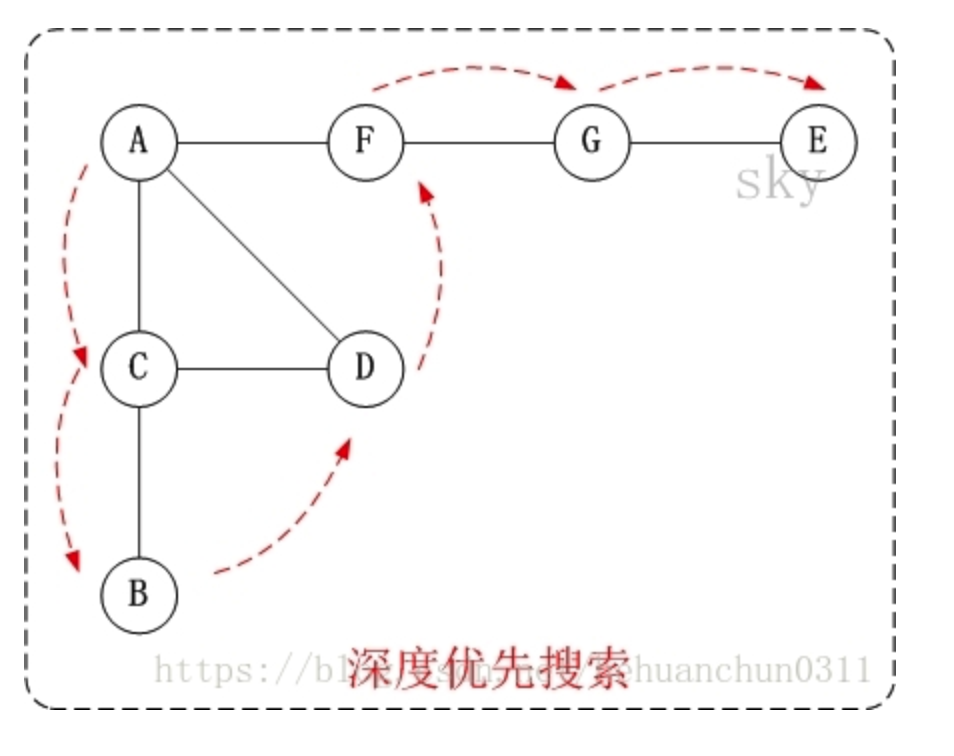
2 无向图深度优先
对上面的图G1进行深度优先遍历,从顶点A开始。
第1步:访问A。
第2步:访问(A的邻接点)C。在第1步访问A之后,接下来应该访问的是A的邻接点,即”C,D,F”中的一个。在本文的实现中,顶点ABCDEFG是按照顺序存储,C在”D和F”的前面,因此,先访问C。
第3步:访问(C的邻接点)B。在第2步访问C之后,接下来应该访问C的邻接点,即”B和D”中一个(A已经被访问过,就不算在内)。而由于B在D之前,先访问B。
第4步:访问(C的邻接点)D。
第5步:访问(A的邻接点)F。
第6步:访问(F的邻接点)G。
第7步:访问(G的邻接点)E。
访问顺序是:A -> C -> B -> D -> F -> G -> E
2.2 广度优先 1 介绍 从图中某顶点v出发,在访问了v之后依次访问v的各个未曾访问过的邻接点,然后分别从这些邻接点出发依次访问它们的邻接点,并使得“先被访问的顶点的邻接点先于后被访问的顶点的邻接点被访问,直至图中所有已被访问的顶点的邻接点都被访问到。如果此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则需要另选一个未曾被访问过的顶点作为新的起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。换句话说,广度优先搜索遍历图的过程是以v为起点,由近至远。
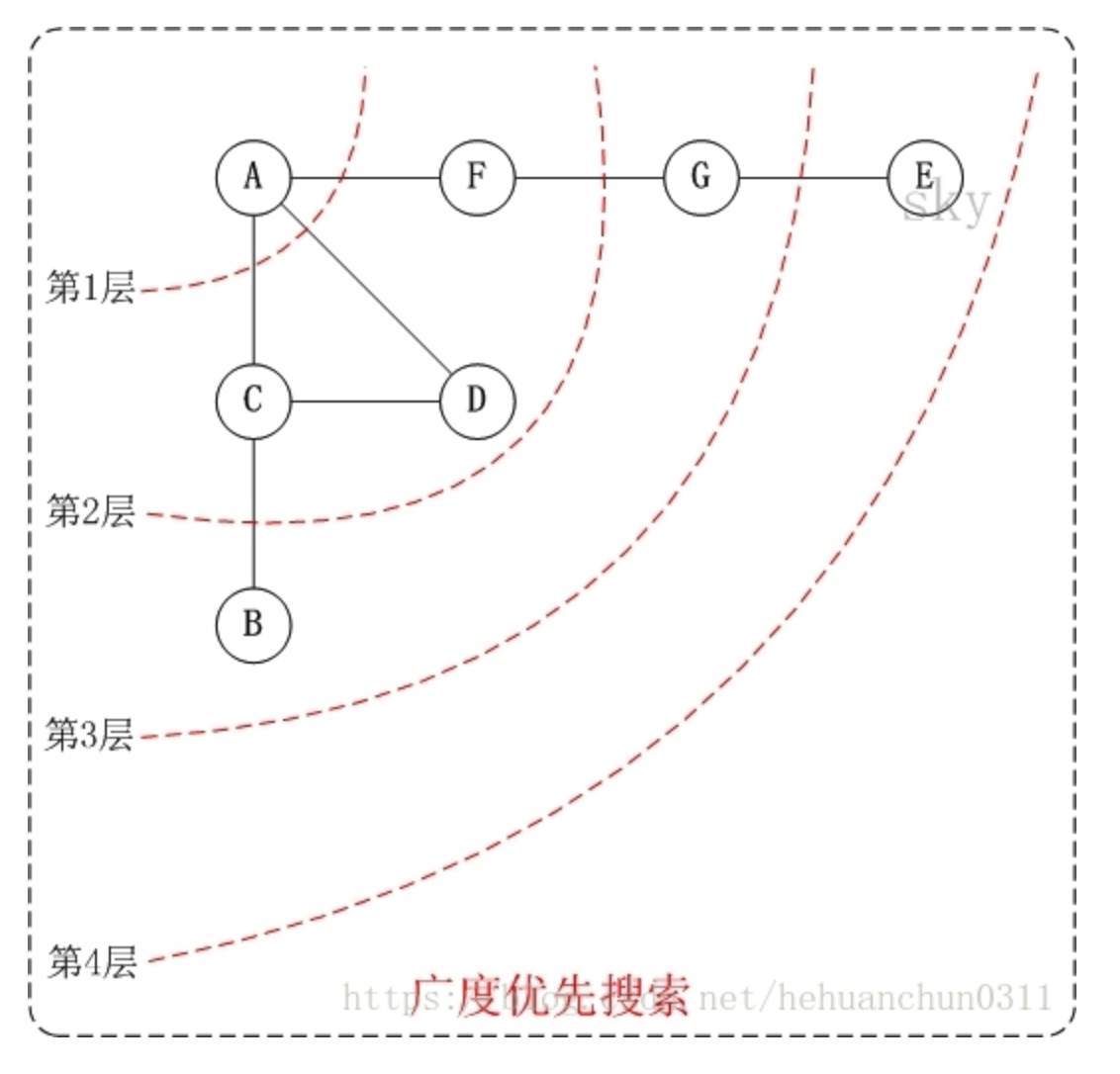
2 无向图广度优先
访问顺序是:A -> C -> D -> F -> B -> G -> E
3 实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 public class GraphSearch <T > public StringBuffer searchPathDFS = new StringBuffer(); public StringBuffer searchPathBFS = new StringBuffer(); public void searchDFS (GraphNode<T> root) if (root == null ) { return ; } if (searchPathDFS.length() > 0 ) { searchPathDFS.append("->" ); } searchPathDFS.append(root.data.toString()); root.visited = true ; for (GraphNode<T> node : root.neighborList) { if (!node.visited) { searchDFS(node); } } } public void searchBFS (GraphNode<T> root) IQueue<GraphNode<T>> queue = new Queue<GraphNode<T>>(); if (searchPathBFS.length() > 0 ) { searchPathBFS.append("->" ); } searchPathBFS.append(root.data.toString()); root.visited = true ; queue.enqueue(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { GraphNode<T> r = queue.dequeue(); for (GraphNode<T> node : r.neighborList) { if (!node.visited) { searchPathBFS.append("->" ); searchPathBFS.append(node.data.toString()); node.visited = true ; queue.enqueue(node); } } } } } public class GraphSearchTest GraphNode<Integer> node1; GraphNode<Integer> node2; GraphNode<Integer> node3; GraphNode<Integer> node4; GraphNode<Integer> node5; GraphNode<Integer> node6; GraphNode<Integer> node7; GraphNode<Integer> node8; GraphNode<Integer> node9; GraphNode<Integer> node10; @Before public void before () node1 = new GraphNode<Integer>(1 ); node2 = new GraphNode<Integer>(2 ); node3 = new GraphNode<Integer>(3 ); node4 = new GraphNode<Integer>(4 ); node5 = new GraphNode<Integer>(5 ); node6 = new GraphNode<Integer>(6 ); node7 = new GraphNode<Integer>(7 ); node8 = new GraphNode<Integer>(8 ); node9 = new GraphNode<Integer>(9 ); node10 = new GraphNode<Integer>(10 ); node1.neighborList.add(node2); node1.neighborList.add(node3); node2.neighborList.add(node4); node2.neighborList.add(node5); node2.neighborList.add(node6); node3.neighborList.add(node1); node3.neighborList.add(node6); node3.neighborList.add(node7); node3.neighborList.add(node8); node4.neighborList.add(node2); node4.neighborList.add(node5); node5.neighborList.add(node2); node5.neighborList.add(node4); node5.neighborList.add(node6); node6.neighborList.add(node2); node6.neighborList.add(node5); node6.neighborList.add(node3); node6.neighborList.add(node8); node6.neighborList.add(node9); node6.neighborList.add(node10); node7.neighborList.add(node3); node8.neighborList.add(node3); node8.neighborList.add(node6); node8.neighborList.add(node9); node9.neighborList.add(node6); node9.neighborList.add(node8); node9.neighborList.add(node10); node10.neighborList.add(node6); node10.neighborList.add(node9); } @Test public void searchDFSTest () GraphSearch<Integer> graphSearch = new GraphSearch<Integer>(); graphSearch.searchDFS(node1); String expectedSearchPath = "1->2->4->5->6->3->7->8->9->10" ; Assert.assertEquals(expectedSearchPath, graphSearch.searchPathDFS.toString()); } @Test public void searchBFSTest () GraphSearch<Integer> graphSearch = new GraphSearch<Integer>(); graphSearch.searchBFS(node1); String expectedSearchPath = "1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->10" ; Assert.assertEquals(expectedSearchPath, graphSearch.searchPathBFS.toString()); } }