AOP是Spring Core中几大重要能力之一,我们可以使用AOP实现很多功能,比如我们常用的日志处理与Spring中的声明式事务。
简介 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),即面向切面编程
AOP把软件系统分为两个部分:核心关注点 和横切关注点 。业务处理的主要流程是核心关注点,与之关系不大的部分是横切关注点。横切关注点的一个特点是,他们经常发生在核心关注点的多处,而各处基本相似,比如权限认证、日志、事物。AOP的作用在于分离系统中的各种关注点,将核心关注点和横切关注点分离开来 。
基本介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 1 、横切关注点(对哪些方法进行切入)对哪些方法进行拦截,拦截后怎么处理,这些关注点称之为横切关注点 2 、切面(aspect,把原来糅杂在业务逻辑代码中的非业务代码抽取出来,把功能相同的放在一个类中形成一个切面)类是对物体特征的抽象,切面就是对横切关注点的抽象 3 、连接点(joinpoint)(需要切入的点)被拦截到的点,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点指的就是被拦截到的方法,实际上连接点还可以是字段或者构造器 4 、切入点(pointcut)对连接点进行拦截的定义 5 、通知(advice)所谓通知指的就是指拦截到连接点之后要执行的代码,通知分为前置、后置、异常、最终、环绕通知五类 6 、目标对象代理的目标对象 7 、织入(weave)将切面应用到目标对象并导致代理对象创建的过程 8 、引入(introduction)在不修改代码的前提下,引入可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或字段
简单案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 public interface Calculate int add (int numA,int numB) int reduce (int numA,int numB) int div (int numA,int numB) int multi (int numA,int numB) } =====================实现类 public class TulingCalculate implements Calculate public int add (int numA, int numB) return numA+numB; } public int reduce (int numA, int numB) return numA-numB; } public int div (int numA, int numB) return numA/numB; } public int multi (int numA, int numB) return numA*numB; } } =====================切面类===================== @Aspect public class TulingLogAspect @Pointcut("execution(* com.tuling.TulingCalculate.*(..))") public void pointCut () @Before(value = "pointCut()") public void methodBefore (JoinPoint joinPoint) String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("执行目标方法【" +methodName+"】之前执行<前置通知>,入参" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); } @After(value = "pointCut()") public void methodAfter (JoinPoint joinPoint) String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("执行目标方法【" +methodName+"】之前执行<后置通知>,入参" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); } @AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()") public void methodReturning (JoinPoint joinPoint ) String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("执行目标方法【" +methodName+"】之前执行<返回通知>,入参" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); } @AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()") public void methodAfterThrowing (JoinPoint joinPoint) String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("执行目标方法【" +methodName+"】之前执行<异常通知>,入参" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); } } ===========================配置类============= @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class MainConfig @Bean public Calculate calculate () return new TulingCalculate(); } @Bean public TulingLogAspect tulingLogAspect () return new TulingLogAspect(); } }
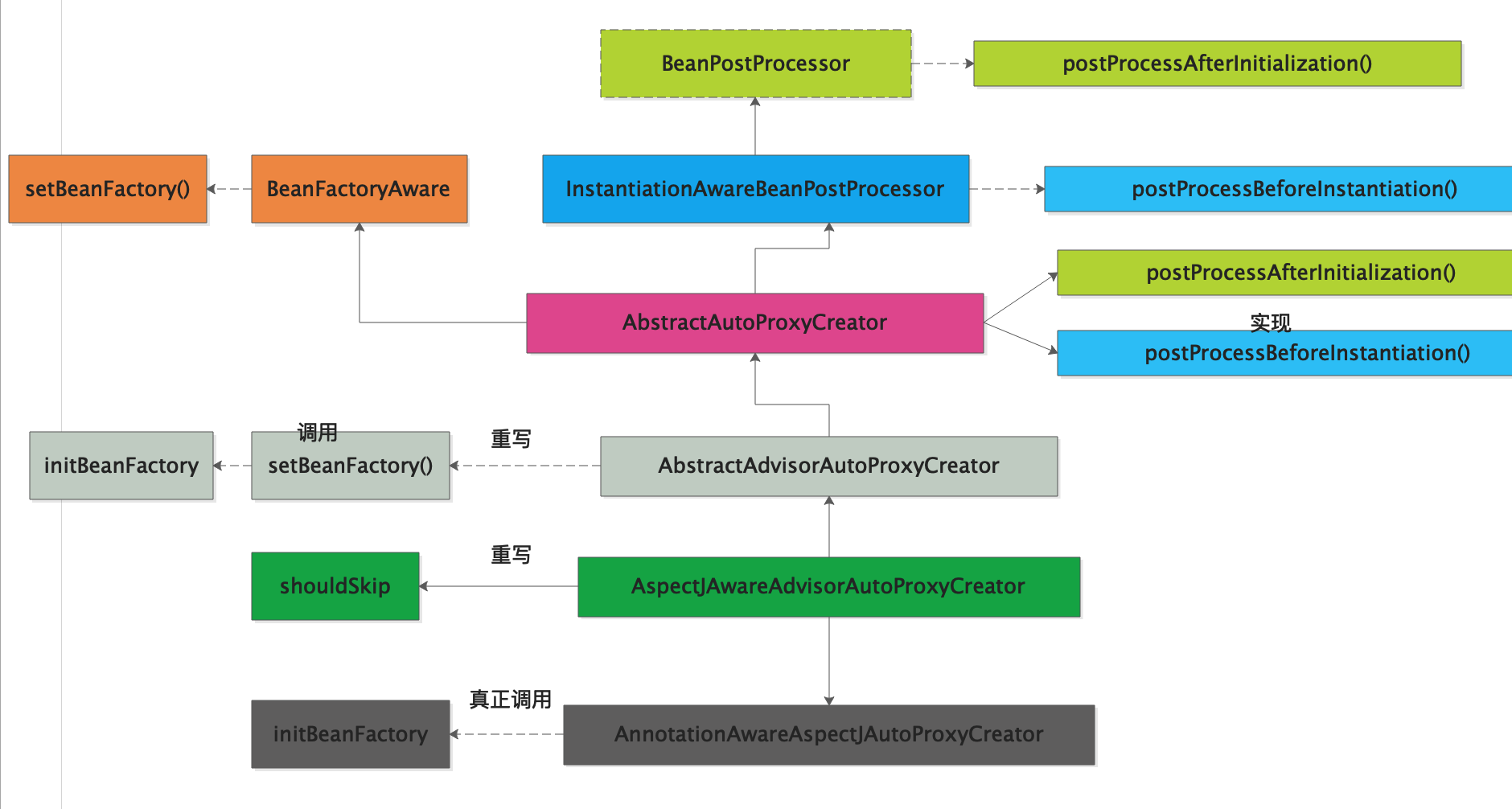
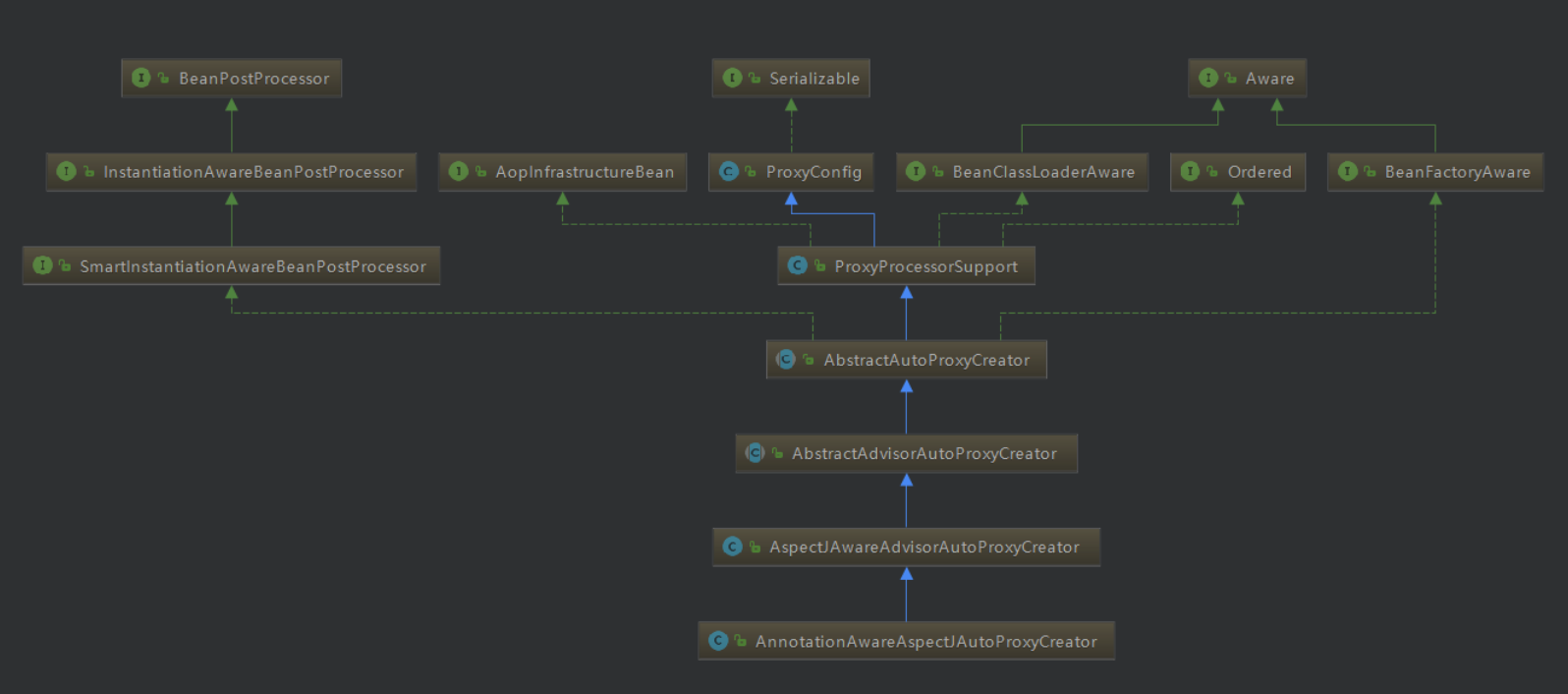
Aop 流程图 继承结构功能分析图:
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的作用
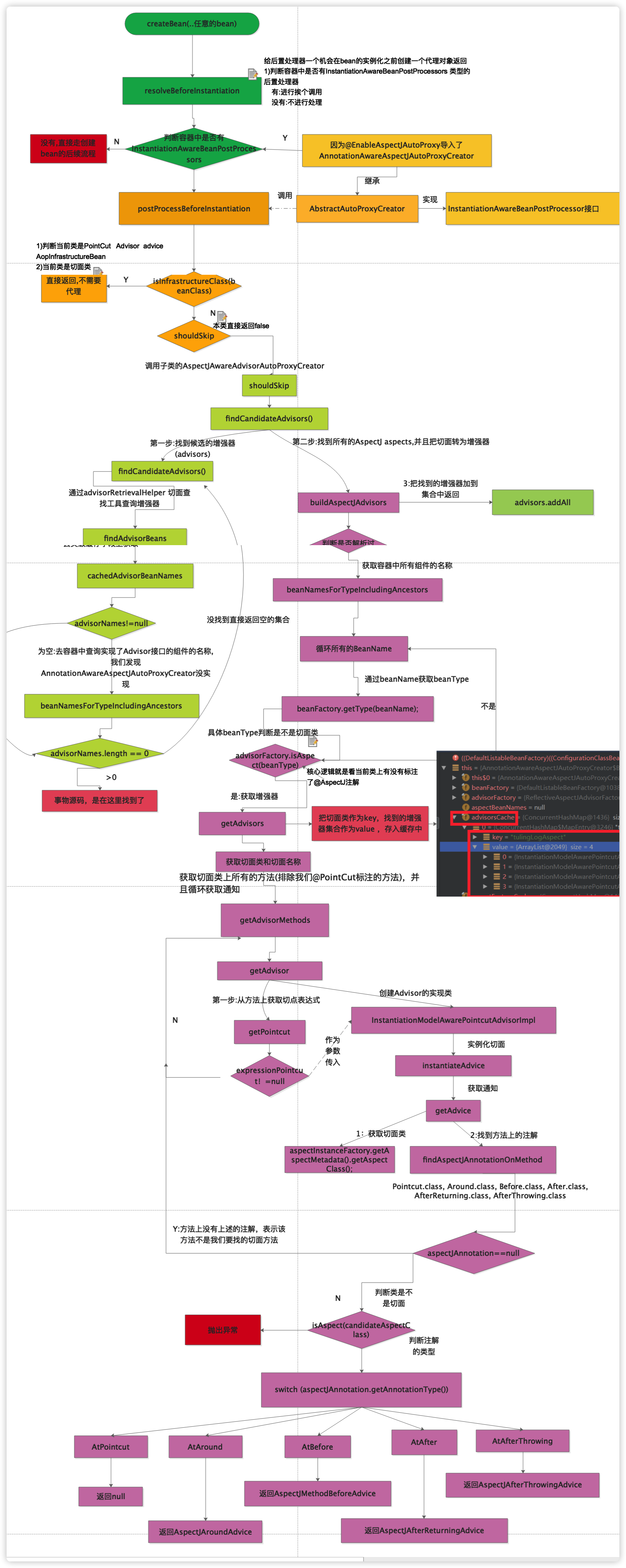
BeanPostProceesor创建代理对象流程
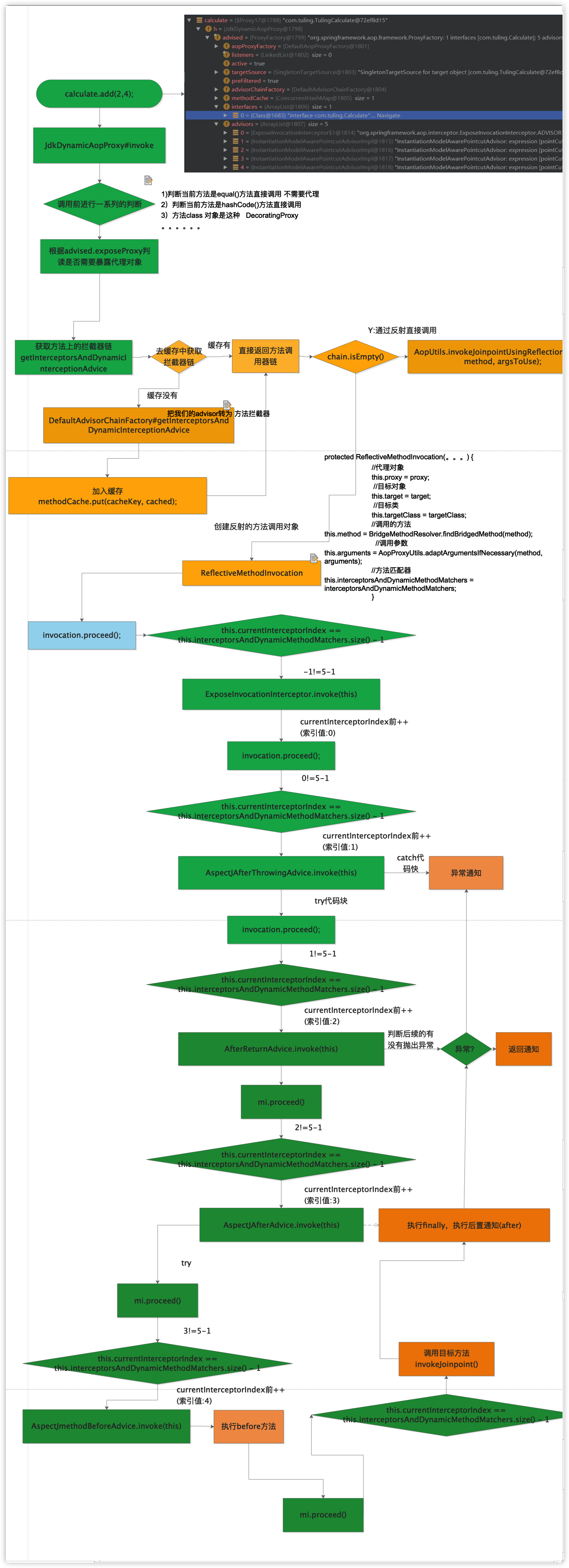
Aop 代理对象调用流程图
源码分析 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 配置类上加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启AOP
我们发现@EnableAspectJAutoProxy上标注了一个@Import注解,我们知道@Import可以给我们容器中添加组件
1 2 3 4 5 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class) public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 经过跟踪源代码我们发现,AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口
凡是实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar可以给我们容器中添加bean定义信息
作用:往容器中注册了一个名称叫org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator
**类型为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 注解的apsectj自动代理创建器**1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions (AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry); AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class); if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass" )) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); } if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy" )) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry); } } } ====AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);===== public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) return registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry, null ); } public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source); } private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired (Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null" ); if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) { BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME); if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) { int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName()); int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls); if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) { apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName()); } } return null ; } RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls); beanDefinition.setSource(source); beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order" , Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE); beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition); return beanDefinition; }
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
根据上诉类图
1)AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 有实现了Aware接口的特性(BeanFactoryAware)
2)AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了BeanPostProcessor接口(后置处理器的特性)
3)AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口(后置处理器的一种,在实例化之前进行调用)
现在分析AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 的功能
实现BeanFactoryAware 3.1)所以我们首先来分析AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了BeanFactoryAware接口 做了什么工作?
①:org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了BeanFactoryAware
我们查看源码的时候发现AbstractAutoProxyCreator 的setBeanFactory()方法啥都没有做,但是又被子类覆盖了
1 2 3 4 @Override public void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) this .beanFactory = beanFactory; }
②:AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator覆盖了AbstractAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory()方法
做了二件事情
1:调用父类的super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
2:调用本来的initBeanFactory((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory);初始化bean工厂方法
但是本类的AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory()又被子类覆盖了1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) super .setBeanFactory(beanFactory); if (!(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "AdvisorAutoProxyCreator requires a ConfigurableListableBeanFactory: " + beanFactory); } initBeanFactory((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory); } protected void initBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) this .advisorRetrievalHelper = new BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter(beanFactory); }
③:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator#initBeanFactory覆盖了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 protected void initBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) super .initBeanFactory(beanFactory); if (this .aspectJAdvisorFactory == null ) { this .aspectJAdvisorFactory = new ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory(beanFactory); } this .aspectJAdvisorsBuilder = new BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter(beanFactory, this .aspectJAdvisorFactory); }
总结:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了BeanFactoryAware 也是做了二个事情
事情1:把Beanfactory 保存到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 组件上.
事情2: 为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 的aspectJAdvisorsBuilder aspect增强器构建器赋值
实现BeanPostProcessor 3.2)还发现了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了BeanPostProcessor接口(后置处理器的特性)
我们追根溯源 AbstractAutoProxyCreator类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口 所以我们分析BeanPostProcessor的二个方法
①:postProcessBeforeInitialization初始化之前的方法 貌似什么都没有干
1 2 3 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) return bean; }
②:postProcessAfterInitialization 这个方法很重要 后面单独说(创建代理对象的逻辑)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException if (bean != null ) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this .earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 3.3)还发现了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口(后置处理器的一种,在实例化之前进行调用)
我们追根溯源 AbstractAutoProxyCreator类实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口 所以我们分析SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的二个方法
①postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (beanName == null || !this .targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { if (this .advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null ; } if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null ; } } if (beanName != null ) { TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null ) { this .targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this .proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } } return null ; } ===========判断是不是基础的bean======================================= protected boolean isInfrastructureClass (Class<?> beanClass) boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass); if (retVal && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]" ); } return retVal; }
②:postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
1 2 3 4 @Override public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation (Object bean, String beanName) return true ; }
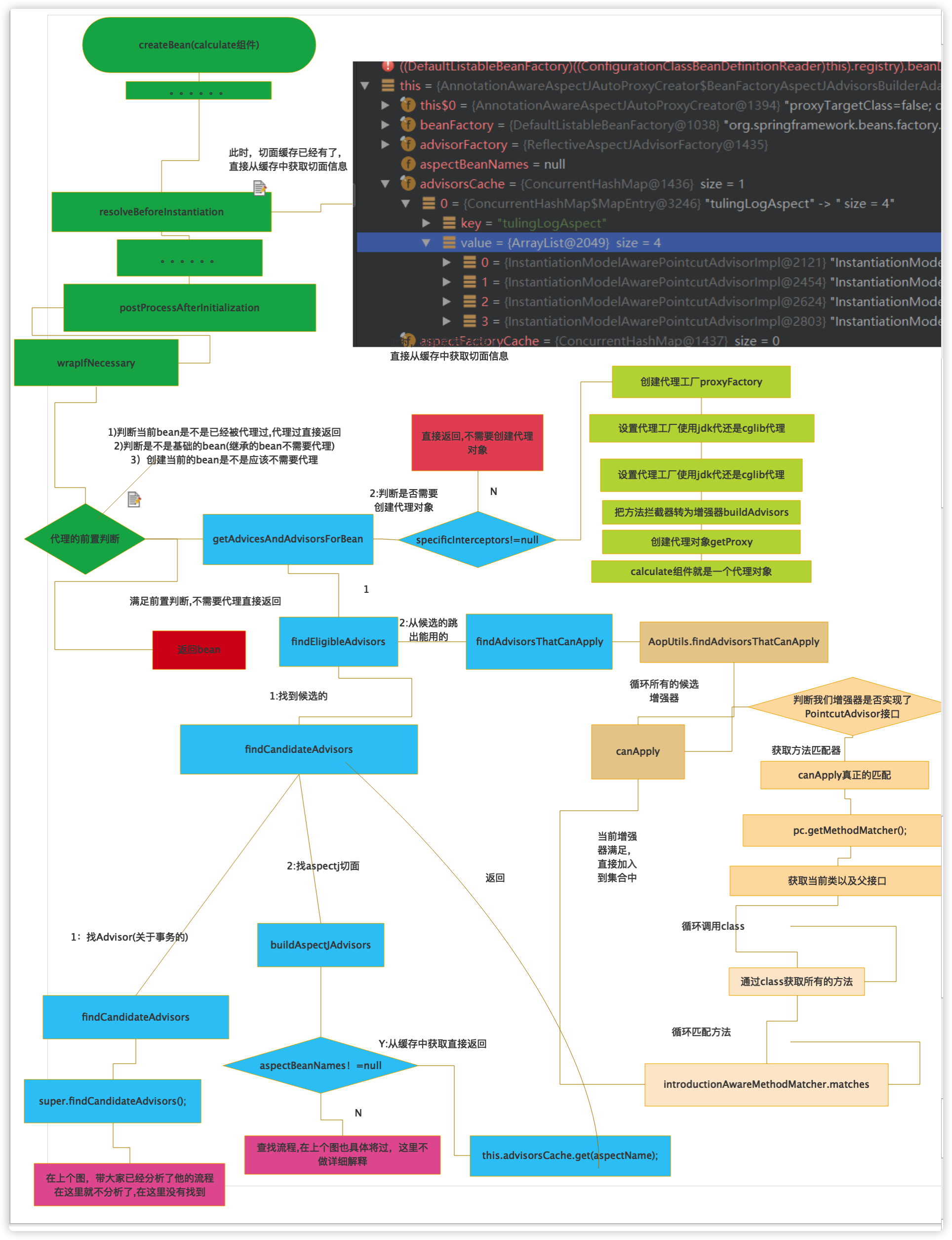
真正的创建代理 真正的创建代理对象从BeanPostProcessor处理器的后置方法开始
1:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
2:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary 有必要的话进行包装
3:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
4:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors
5:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
6:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy创建代理对象
4.1):>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException if (bean != null ) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this .earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
4.2):>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 protected Object wrapIfNecessary (Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) if (beanName != null && this .targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this .advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null ); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this .proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } protected boolean isInfrastructureClass (Class<?> beanClass) boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass); if (retVal && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]" ); } return retVal; }
4.3:>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
4.4)org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
4.5)org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors 从IOC容器中查找所有的增强器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors () List<Advisor> advisors = super .findCandidateAdvisors(); advisors.addAll(this .aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); return advisors; } ============super .findCandidateAdvisors();================================= public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans () String[] advisorNames = this .cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null ) { advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this .beanFactory, Advisor.class, true , false ); this .cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } if (advisorNames.length == 0 ) { return new ArrayList<Advisor>(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<Advisor>(); for (String name : advisorNames) { if (isEligibleBean(name)) { if (this .beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'" ); } } else { try { advisors.add(this .beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class)); } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause(); if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) { BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause; if (this .beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bce.getBeanName())) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name + "' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage()); } continue ; } } throw ex; } } } } return advisors; } ====aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()解析@Aspject 的==================== 下面buildAspectJAdvisors这个方法为我们做了什么? 第一步:先从增强器缓存中获取增强器对象 判断缓存中有没有增强器对象,有,那么直接从缓存中直接获取返回出去 没有.....从容器中获取所有的beanName 遍历上一步获取所有的beanName,通过beanName获取beanType 根据beanType判断当前bean是否是一个的Aspect注解类,若不是则不做任何处理 调用advisorFactory.getAdvisors获取通知器 public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors () List<String> aspectNames = this .aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null ) { synchronized (this ) { aspectNames = this .aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null ) { List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); aspectNames = new LinkedList<String>(); String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this .beanFactory, Object.class, true , false ); for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) { continue ; } Class<?> beanType = this .beanFactory.getType(beanName); if (beanType == null ) { continue ; } if (this .advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) { aspectNames.add(beanName); AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName); if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) { MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this .beanFactory, beanName); List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this .advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory); if (this .beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { this .advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors); } else { this .aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory); } advisors.addAll(classAdvisors); } else { if (this .beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName + "' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton" ); } MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this .beanFactory, beanName); this .aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory); advisors.addAll(this .advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)); } } } this .aspectBeanNames = aspectNames; return advisors; } } } if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (String aspectName : aspectNames) { List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this .advisorsCache.get(aspectName); if (cachedAdvisors != null ) { advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors); } else { MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this .aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName); advisors.addAll(this .advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)); } } return advisors; } public List<Advisor> getAdvisors (MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName(); validate(aspectClass); MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory = new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory); List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<Advisor>(); for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) { Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName); if (advisor != null ) { advisors.add(advisor); } } if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) { Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory); advisors.add(0 , instantiationAdvisor); } for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) { Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field); if (advisor != null ) { advisors.add(advisor); } } return advisors; } public Advisor getAdvisor (Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut( candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); if (expressionPointcut == null ) { return null ; } return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod, this , aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName); } private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut (Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); if (aspectJAnnotation == null ) { return null ; } AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp = new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0 ], new Class<?>[0 ]); ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression()); ajexp.setBeanFactory(this .beanFactory); return ajexp; } protected static AspectJAnnotation<?> findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) { for (Class<?> clazz : ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES) { AspectJAnnotation<?> foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class<Annotation>) clazz); if (foundAnnotation != null ) { return foundAnnotation; } } return null ; } public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl (AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut, Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) this .declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut; this .declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass(); this .methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName(); this .parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes(); this .aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod; this .aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory; this .aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory; this .declarationOrder = declarationOrder; this .aspectName = aspectName; if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) { Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union( aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this .declaredPointcut); this .pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut( this .declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); this .lazy = true ; } else { this .pointcut = this .declaredPointcut; this .lazy = false ; this .instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this .declaredPointcut); } } public Advice getAdvice (Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); validate(candidateAspectClass); AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); if (aspectJAnnotation == null ) { return null ; } if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) { throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " + "Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" + candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]" ); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice; switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) { case AtPointcut: if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'" ); } return null ; case AtAround: springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break ; case AtBefore: springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break ; case AtAfter: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break ; case AtAfterReturning: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) { springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning()); } break ; 是不是异常通知 case AtAfterThrowing: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) { springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing()); } break ; default : throw new UnsupportedOperationException( "Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName); springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder); String[] argNames = this .parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod); if (argNames != null ) { springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames); } springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings(); return springAdvice; }
4.5..:)>org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply ( List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName); try { return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass); } finally { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null ); } } public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply (List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { continue ; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; } public static boolean canApply (Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { return true ; } } public static boolean canApply (Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null" ); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false ; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { return true ; } IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null ; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); classes.add(targetClass); for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); for (Method method : methods) { if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null && introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) || methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true ; } } } return false ; }
4.6)org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy创建代理对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 protected Object createProxy ( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) if (this .beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this .beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this ); if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true ); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this .freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true ); } return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); } public Object getProxy (ClassLoader classLoader) return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); } public AopProxy createAopProxy (AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null ) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation." ); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { jdk代理 return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } } public Object getProxy (ClassLoader classLoader) if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this .advised.getTargetSource()); } Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this .advised, true ); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this ); }
代理对象调用目标方法 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true) 这个东东是用来干什么的?
没有配置exposeProxy 暴露代理对象的时候我们方法调用
我们在Mod方法中 通过this来调用本类的方法add()方法的时候,发现add()的方法不会被拦截
而我们配置了后exposeProxy的属性,我们发现可以通过
int retVal = ((Calculate) AopContext.currentProxy()).add(numA,numB);
调用的时候,发现了add()方法可以被拦截
原理:把这个exposeProxy设置为true,会把代理对象存放在线程变量中,
AopContext.currentProxy())是从线程变量中获取代理对象(源码中分析)
应用场景(事物方法调用事物方法需要二个都起作用需要配置这个东东)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public interface Calculate int add (int numA,int numB) int reduce (int numA,int numB) int div (int numA,int numB) int multi (int numA,int numB) int mod (int numA,int numB) } public class TulingCalculate implements Calculate public int add (int numA, int numB) return numA+numB; } public int reduce (int numA, int numB) return numA-numB; } public int div (int numA, int numB) return numA/numB; } public int multi (int numA, int numB) return numA*numB; } public int mod (int numA,int numB) int retVal = ((Calculate) AopContext.currentProxy()).add(numA,numB); return retVal%numA; } }
代理对象调用源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable MethodInvocation invocation; Object oldProxy = null ; boolean setProxyContext = false ; TargetSource targetSource = this .advised.targetSource; Class<?> targetClass = null ; Object target = null ; try { Object retVal; if (this .advised.exposeProxy) { oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true ; } target = targetSource.getTarget(); if (target != null ) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } List<Object> chain = this .advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); if (chain.isEmpty()) { Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); retVal = invocation.proceed(); } Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } } ====org.springframework.aop.framework.AdvisedSupport#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice=========== 把增强器中转为方法拦截器链 public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice (Method method, Class<?> targetClass) MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method); List<Object> cached = this .methodCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached == null ) { cached = this .advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( this , method, targetClass); this .methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached); } return cached; } ==org.springframework.aop.framework.AdvisorChainFactory#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice==== public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice ( Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length); Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass); AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) { if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher(); if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) { MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); if (mm.isRuntime()) { for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm)); } } else { interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } } } else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } else { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } return interceptorList; }