Nginx应用指南
1 Nginx应用指南 1 Nginx 特点 IO多路复用epoll
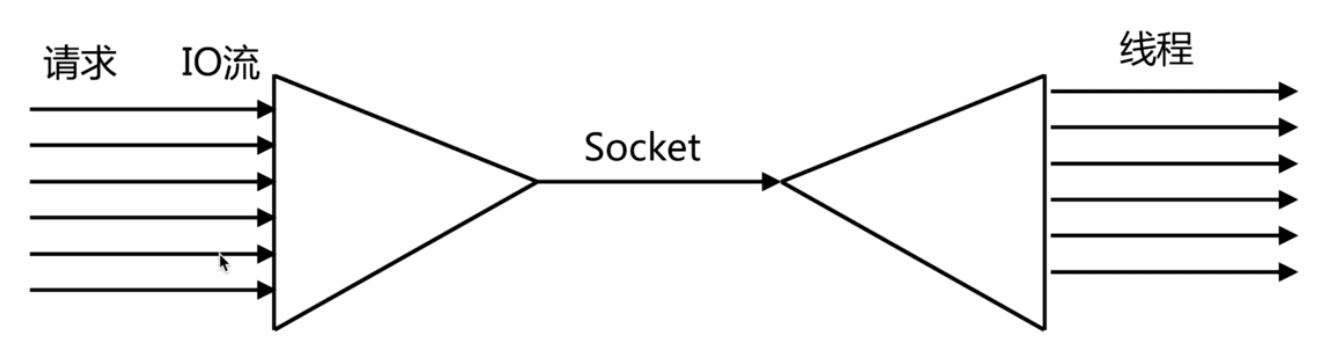
多个描述符的 I/O 操作都能在一个线程内并发交替地顺序完成,这就叫I/O多路复用,这里的”复用”指的是复用同一个线程。
轻量级
功能模块少:
CPU亲和(affinity)
nginx正是利用到了cpu的亲和来提高并发处理能力以及减少不必要的cpu损耗。
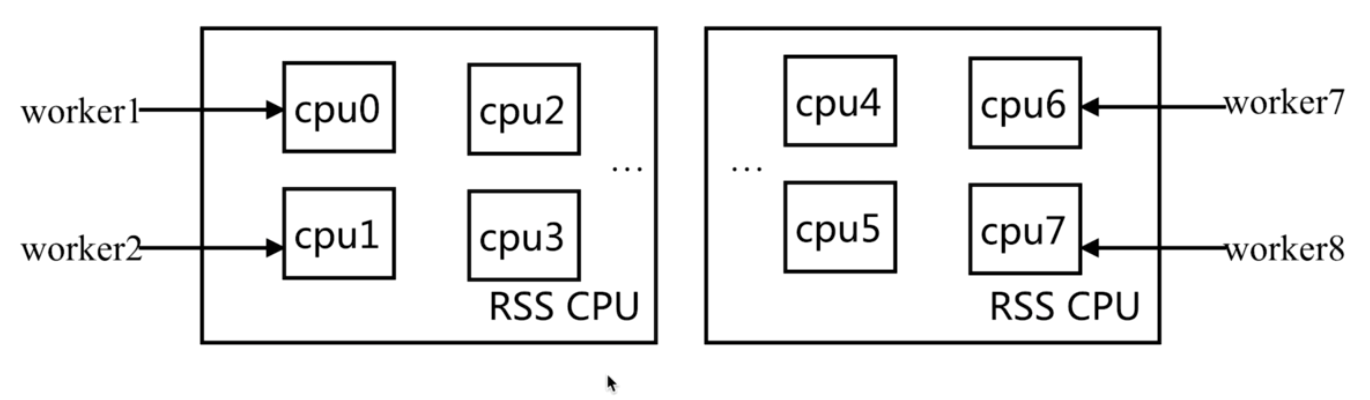
1.什么是CPU亲和
nginx作为接入层的中间件,nginx通过多个work进程进行处理。
假设我们主机是两个CPU,每个有四个核心,我们把CPU的八个进程分别绑定到不同的CPU上(也就是不同的work分配到不同的核心上)。如果有多个CPU利用自带的CPU切换,会造成性能损失。利用这种CPU的亲和绑定,就能减少切换的损耗。
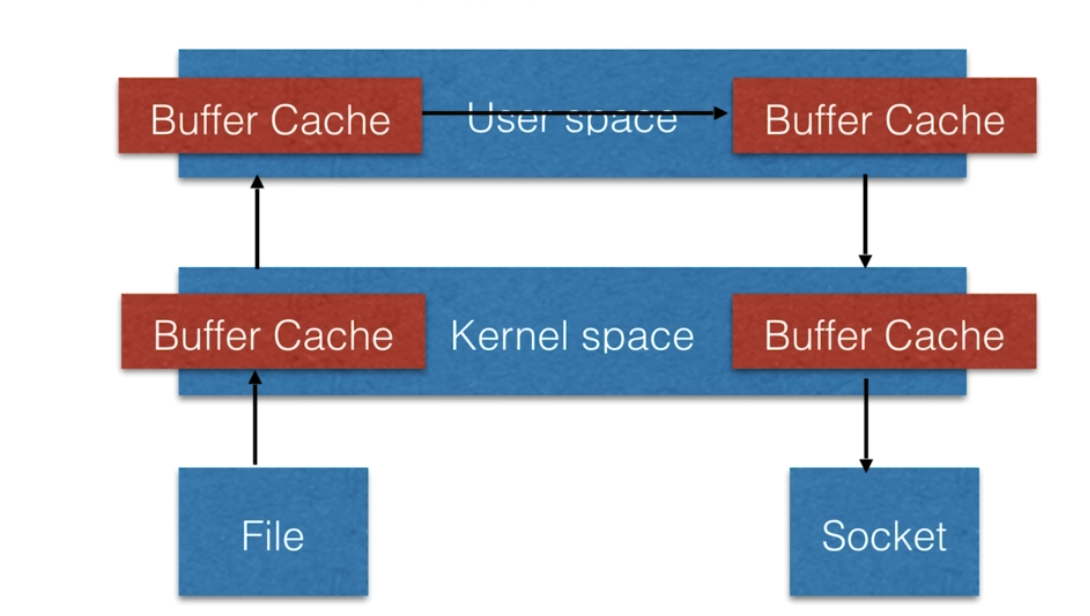
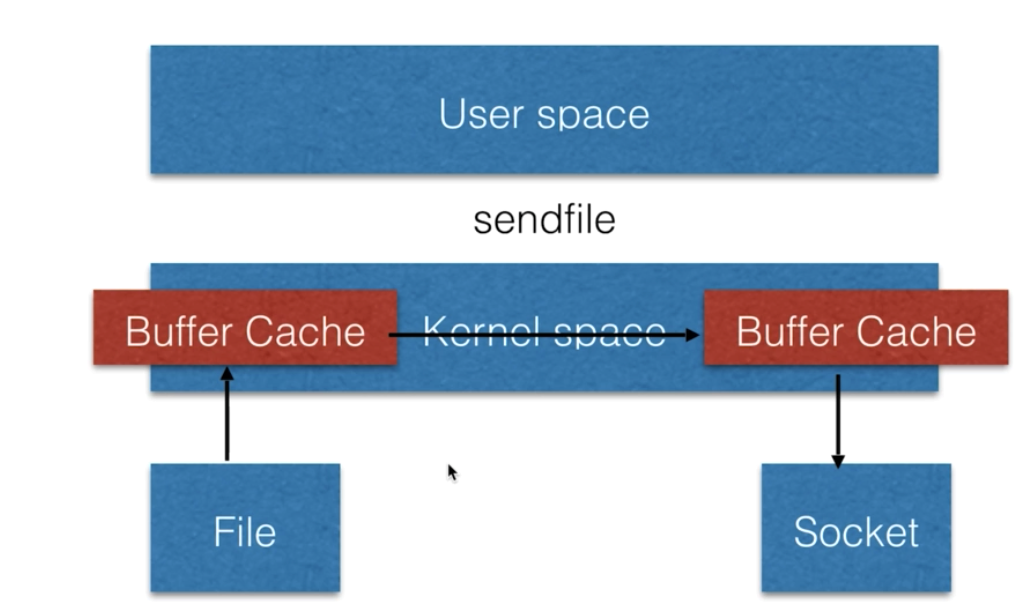
sendfile
nginx采用sendfile机制处理静态文件,因此效率很高。
上图是传统的http服务,当我们访问一个文件时,会先经过内核空间,再经过用户空间,传给socket,最后通过response返回给用户。该过程需要多次与用户空间进行切换,但是静态文件其实不需要与用户空间进行过多的逻辑处理。直接可以通过内核空间传输。
sendfile机制只通过内核空间,将文件传给socket,最终响应给用户。
2 Nginx安装及启动 1 配置yum源安装 To set up the yum repository, create the file named /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo with the following contents:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 >[nginx-stable] >name=nginx stable repo >baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ >gpgcheck=1 >enabled=1 >gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key >[nginx-mainline] >name=nginx mainline repo >baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ >gpgcheck=1 >enabled=0 >gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
By default, the repository for stable nginx packages is used. If you would like to use mainline nginx packages, run the following command:
1 sudo yum-config-manager --enable nginx-mainline
To install nginx, run the following command:
2 常用命令 查看nginx版本: nginx -v
显示 nginx 的版本,编译器版本和配置参数: nginx -V
查看nginx.conf配置文件目录 : nginx -t
Nginx启动命令: service nginx star
重新加载配置文件: nginx -s reload
检测配置文件: nginx -t
3 常用变量
变量名
描述
$uri
请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数)
$request_uri
请求中的当前URI(带完整路径)
$host
HTTP请求行的主机名>”HOST”请求头字段>符合请求的服务器名
$hostname
主机名
$remote_addr
客户端地址
$remote_port
客户端端口
$remote_user
用于HTTP基础认证服务的用户名
$request_filename
当前连接请求的文件路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成
$request_method
HTTP请求方法,通常为”GET”或”POST”
$server_addr
服务器端地址,需要注意的是:为了避免访问linux系统内核,应将ip地址提前设置在配置文件中
$server_name
服务器名
$server_port
服务器端口
$server_protocol
服务器的HTTP版本,通常为 “HTTP/1.0” 或 “HTTP/1.1”
$scheme
请求使用的Web协议,”http” 或 “https”
$http_HEADER
匹配请求报文中指定的HEADER
$http_host
匹配请求报文中host首部
$document_root
当前请求映射到的root配置
2 基础配置 1 Nginx配置文件 Nginx主配置文件/etc/nginx/nginx.conf是一个纯文本类型的文件,整个配置文件是以区块的形式组织的。一般每个区块以一对大括号{}来表示开始与结束
Main位于Nginx.conf配置文件的最高层
Main层下可以有Event、HTTP层
HTTP层下面有允许有多个Server层,用于对不同的网站做不同的配置
Server层也允许有多个Location,用户对不同的路径进行不同模块的配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 // nginx默认配置语法 worker_processes // nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数 error_log // 错误日志 pid // 进程文件 // events事件模块 events { //事件模块 worker_connections 1024 // 单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数) use epoll // 事件模型 select | poll } // 非虚拟主机配置或公共配置定义在HTTP{}段内,server段外 http { ... //必须使用虚拟主机配置站点,每个虚拟主机使用一个server{}段 server { listen 80; //监听端口,默认80 server_name localhost; //提供服务的域名或主机名 //控制网站访问路径 location / { root /usr/share/nginx/html; //存放网站 index index.html index.html; // 默认主页 } } }
2 日志模块 Nginx日志对于统计、系统服务排错很有用。Nginx日志主要分为两种:access_log(访问日志)和error_log(错误日志)。通过访问日志我们可以得到用户的IP地址、浏览器的信息,请求的处理时间等信息。错误日志记录了访问出错的信息,可以帮助我们定位错误的原因。本文将详细描述一下如何配置Nginx日志。
基本用法:
access_log /var/logs/nginx-access.log
该例子指定日志的写入路径为/var/logs/nginx-access.log,日志格式使用默认的combined。
1 >access_log /var/logs/nginx-access.log buffer=32k gzip flush=1m
该例子指定日志的写入路径为/var/logs/nginx-access.log,日志格式使用默认的combined,指定日志的缓存大小为32k,日志写入前启用gzip进行压缩,压缩比使用默认值1,缓存数据有效时间为1分钟。
配置示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 access_log /var/logs/nginx-access.log buffer=32k gzip flush=1m access_log /var/logs/nginx-access.log main log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
3 状态监控模块 server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /mystatus {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}#stub_status on; 在1.7.5之前的版本中,指令语法需要任意参数。例如这个
#access_log off; 不写入日志。
访问:
1 2 3 4 Active connections: 1 server accepts handled requests 17 17 14 Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
状态参数介绍Active connections:1 连接数为1,并发连接数。 单位时间内服务器正在处理的连接数。server: nginx启动到现在共处理了几个连接。 accepts: nginx启动到现在共成功创建几次握手。handled requests: 总共处理了几次请求。reading: nginx读取到客户端的Header信息数。writing: nginx返回给客户端的header信息数。waiting: nginx已经处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接。再开启keepalive下active-(reading+writing)
4 下载站点 Syntax : autoindex on | off
Default : autoindex off
Context: http, server, location
// autoindex 常用参数
autoindex_exact_size off
默认on,显示出文件的确切大小,单位是bytes
修改为off, 显示出文件的大概大小,单位是kb或者mb或者gb
autoindex_localtime on
默认为off,显示的文件时间为GMT时间,
修改为on,显示的文件时间为文件的服务器时间
charset utf-8,gbk
默认中文目录乱码,添加上解决乱码
配置示例:
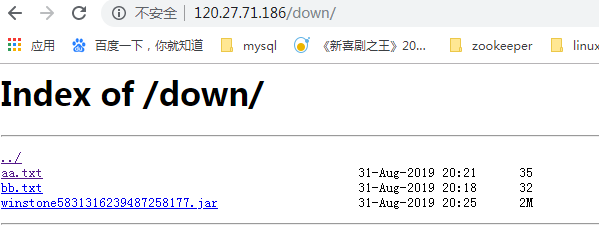
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 location /down { root /soft/package/src; autoindex on; autoindex_exact_size off; autoindex_localtime on; charset utf-8,gbk; }
在对应的文件夹里新建如下文件:
1 2 3 4 5 [root@izm5e7klp5h59pozbv3fghz down]# pw /soft/package/src/down [root@izm5e7klp5h59pozbv3fghz down]# ls aa.txt bb.txt winstone5831316239487258177.jar [root@izm5e7klp5h59pozbv3fghz down]#
访问:120.27.71.186/down
5 请求限制 1 请求频率限制 语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Syntax: limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=rate; Default: — Context: http Syntax: limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay]; Default: — Context: http, server, location
用法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 http { # ...其它代码省略... # 开辟一个10m的请求空间,命名为one。同一个IP发送的请求,平均每秒只处理一次 limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:1m rate=1r/s; server { ... location /search/ { limit_req zone=one; # 当客户端请求超过指定次数,最多宽限5次请求,并延迟处理,1秒1个请求 # limit_req zone=one burst=5; # 当客户端请求超过指定次数,最多宽限5次请求,并立即处理。 # limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay; } } }
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 yum install -y httpd-tools # 安装压测工具 [root@izm5e7klp5h59pozbv3fghz conf.d]# ab -n 50 -c 20 http://120.27.71.186/index.html # 链接50 并发20 // 压测结果 This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $> Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/ Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/ Benchmarking 120.27.71.186 (be patient).....done Server Software: nginx/1.16.1 Server Hostname: 120.27.71.186 Server Port: 80 Document Path: /index.html Document Length: 612 bytes Concurrency Level: 20 Time taken for tests: 0.007 seconds Complete requests: 50 Failed requests: 49 (Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 49, Exceptions: 0) Write errors: 0 Non-2xx responses: 49 Total transferred: 34557 bytes HTML transferred: 24818 bytes Requests per second: 7115.41 [#/sec] (mean) Time per request: 2.811 [ms] (mean) Time per request: 0.141 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) Transfer rate: 4802.49 [Kbytes/sec] received Connection Times (ms) min mean[+/-sd] median max Connect: 0 1 0.2 1 1 Processing: 1 2 0.4 2 2 Waiting: 0 1 0.3 1 2 Total: 2 2 0.3 2 4 Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms) 50% 2 99% 4 100% 4 (longest request)
2 链接限制 语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size; Default: — Context: http Syntax: limit_conn zone number; Default: — Context: http, server, location
用法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 http { # ...其它代码省略... # 开辟一个10m的连接空间,命名为addr limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m; server { ... location /download/ { # 服务器每次只允许一个IP地址连接 limit_conn addr 1; } } }
链接限制没有请求限制有效
我们前面说过 ,多个请求可以建立在一次TCP链接之上,那么我们对请求的精度限制,当然比对一个链接的限制会更加的有效
因为同一时刻只允许一个请求进入。但同时同一时刻多个请求可以通过一个链接进入。所以请求限制才是比较优的解决方案。
6 访问控制 1 基于IP的访问控制 语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Syntax: allow address | CIDR | unix: | all; Default: — Context: http, server, location, limit_except Syntax: deny address | CIDR | unix: | all; Default: — Context: http, server, location, limit_except address:IP地址,例如:192.168.1.1 CIDR:例如:192.168.1.0/24; unix:Socket方式 all:所有
用法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 server { # ...其它代码省略... location ~ ^/index_1.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; deny 151.19.57.60; # 拒绝这个IP访问 deny 47.96.118.93; # 拒绝这个IP访问 allow all; # 允许其他所有IP访问 } location ~ ^/index_2.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; allow 151.19.57.0/24; # 允许IP 151.19.57.* 访问 deny all; # 拒绝其他所有IP访问 } }
2 基于用户登陆认证 语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 //配置语法 Syntax: auth_basic string| off; Default: auth_basic off; Context: http, server, location, limit_except //⽤用户密码记录配置⽂文件 Syntax: auth_basic_user_file file; Default: - Context: http, server, location, limit_except
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 //需要安装依赖组件 [root@xuliangwei ~]# yum install httpd-tools [root@xuliangwei ~]# htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/auth_conf song # 设置用户名 htpasswd -b /etc/nginx/auth_conf song2 chen1208 # 新增用户名和密码 //可在http,server,location下添加如下信息 auth_basic "Auth access Blog Input your Passwd!"; auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/auth_conf;
配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 server { ... location /down { ... auth_basic 'Down Pelase Username!'; auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/auth_conf; }
7 虚拟主机 所谓虚拟主机,在web服务器器⾥里里是⼀一个独⽴立的⽹网站站点,这个站点对应独⽴立的域名(也可能是IP或端口),具有独⽴立的程序及资源⽬目录,可以独⽴立地对外提供服务供用户访问
1 基于域名配置: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1.创建web站点⽬目录[root@LNMP conf]# mkdir /soft/code/{www,bbs}[root@LNMP conf]# echo "www" > /soft/code/www/index.html [root@LNMP conf]# echo "bbs" > /soft/code/bbs/index.html 2.配置虚拟主机 [root@LNMP conf]# catconf.d/{www,bbs}.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.xuliangwei.com test1.com; root /soft/code/www; ... } server { ... listen 80; server_name bbs.xuliangwei.com; root /soft/code/bbs; }
2 基于端口访问 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 server { listen 8001; server_name localhost; root /soft/code/blog; index index.html index.htm; } server { listen 8002; server_name localhost; root /soft/code/www; index index.html index.htm; }
3 虚拟主机别名 所谓虚拟主机别名,就是虚拟主机设置除了了主域名以外的⼀一个域名,实现⽤用户访问的多个域名对应同一个虚拟主机网站的功能
以www.xuliangwei.com域名的虚拟主机为例例 :
为其增加一个别名xuliangwei.com时,出现网站内容和访问www.xuliangwei.com是一样的,具体配置如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 //默认配置 [root@LNMP ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.xuliangwei.com; } //别名配置 [root@LNMP ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.xuliangwei.com xuliangwei.com; ... } //使用Linux下curl测试结果 [root@LNMP conf]# curl xuliangwei.comwww.xuliangwei.com [root@LNMP conf]# curl www.xuliangwei.comwww.xuliangwei.com //访问带www和不不带www是一样的, 除了了别名实现也可以通过rewrite实现Nginx慢请求日志记录
3 静态资源 1 静态资源类型 Nginx作为静态资源Web服务器器部署配置, 传输非常的高效, 常常用于静态资源处理理, 请求, 动静分离
非服务器器动态运行生成的文件属于静态资源
类型
种类
浏览器器端渲染
HTML、CSS、JS
图片
JPEG、GIF、PNG
视频
FLV、Mp4
文件
TXT、任意下载文件
2 配置语法 1.文件读取高效sendfile
1 2 3 Syntax: sendfile on | off; Default: sendfile off; Context: http, server, location, if in location
2.提高网络传输效率nopush
1 2 3 Syntax: tcp_nopush on | off; Default: tcp_nopush off; Context: http, server, location
作用: sendfile开启情况下, 提高网络包的’传输效率’
3.与tcp_nopush之对应的配置tcp_nodelay
1 2 3 Syntax: tcp_nodelay on | off; Default: tcp_nodelay on; Context: http, server, location
作用: 在keepalive连接下,提高网络的传输’实时性’
3文件压缩 1 gzip压缩配置语法
1 2 3 Syntax: gzip on | off; Default: gzip off; Context: http, server, location, if in location
作用: 传输压缩
2 gzip压缩⽐比率配置语法
1 2 3 Syntax: gzip_comp_level level; Default: gzip_comp_level 1; Context: http, server, location
作用: 压缩本身比较耗费服务端性能
3.gzip压缩协议版本
1 2 3 Syntax: gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1; Default: gzip_http_version 1.1; Context: http, server, location
作用: 压缩使用在http哪个协议, 主流版本1.1
4.扩展压缩模块
1 2 3 Syntax: gzip_static on | off | always; Default: gzip_static off; Context: http, server, location
作用: 预读gzip功能
5.压缩案例配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 server { listen 80; server_name 120.27.71.186; sendfile on; location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ { gzip on; gzip_http_version 1.1; gzip_comp_level 2; gzip_types text/plain application/json application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rsstext/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png; root /soft/code/images; } location ~ .*\.(txt|xml)$ { gzip on; gzip_http_version 1.1; gzip_comp_level 2; gzip_types text/plain application/json application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rsstext/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png; root /soft/code/images; } } # du -sh 12621.txt.0 查看文件大小
4 浏览器缓存 1.缓存配置语法expires
1 2 3 4 Syntax: expires [modified] time; expires epoch | max | off; Default: expires off; Context: http, server, location, ifinlocation
作用: 添加Cache-Control Expires头
2.配置静态资源缓存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 location~ .*\.(js|css|html)$ { root /soft/code/js; expires1h; } location~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ { root /soft/code/images; expires7d; }
3.开发代码没有正式上线时, 希望静态文件不不被缓存
1 2 3 4 5 //取消js css html等静态⽂文件缓存 location ~ .*\.(css|js|swf|json|mp4|htm|html)$ { add_header Cache-Control no-store; add_header Pragma no-cache; }
阿里云缓存策略帮助手册
Nginx静态资源缓存
5 跨域 Nginx跨域访问配置
1 2 3 Syntax: add_header name value [always]; Default: — Context: http, server, location, if in location
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
2.配置Nginx跨域访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 //运⾏行行www.xuliangwei.com域名跨域访问 [root@Nginx conf.d]# cat origin.conf server { listen 80; server_name kt.xuliangwei.com; sendfile on; access_log /var/log/nginx/kuayue.log main; location ~ .*\.(html|htm)$ { add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin http://www.xuliangwei.com; add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS; root /soft/code; } }
6 防盗链 盗链指的是在自己的界⾯面展示不不在自己服务器器上的内容,通过技术手段获得他人服务器器的资源地址,绕过别人资源展示页面,在自己页面向⽤用户提供此内容,从而减轻自己服务器器的负担,因为真实的空间和流量量来自别人服务器器
防盗链设置思路路: 区别哪些请求是非正常用户请求
基于http_refer防盗链配置模块
1 2 3 Syntax: valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | string ...; Default: —Context: server, location
2.启动防盗链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 //⽀支持IP、域名、正则方式 location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ { valid_referers none blocked www.xuliangwei.com; if ($invalid_referer) { return 403; } root /soft/code/images; }
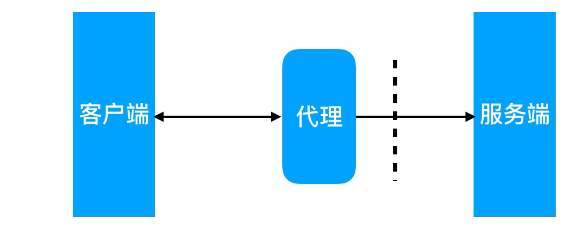
4 代理 1 简介 正向代理理(内部上网) 客户端<–>代理理->服务端
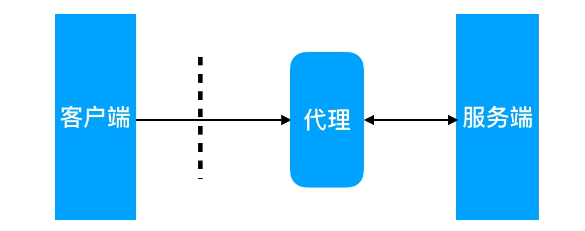
反向代理理客户端->代理理<–>服务端
代理理区别
区别在于代理理的对象不不⼀一样
正向代理理代理理的对象是客户端
反向代理理代理理的对象是服务端
2 Nginx代理理配置语法 1.Nginx代理理配置语法
1 2 3 4 5 6 Syntax: proxy_pass URL; Default: — Context: location, if in location, limit_except http://localhost:8000/uri/ http://192.168.56.11:8000/uri/ http://unix:/tmp/backend.socket:/uri/
2.类似于nopush缓冲区
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 //尽可能收集所有头请求, Syntax: proxy_buffering on | off; Default: proxy_buffering on; Context: http, server, location //扩展: proxy_buffer_size proxy_buffers proxy_busy_buffer_size
3.跳转重定向
1 2 3 4 Syntax: proxy_redirect default; proxy_redirect off;proxy_redirect redirect replacement; Default: proxy_redirect default; Context: http, server, location
4.头信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 Syntax: proxy_set_header field value; Default: proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host; proxy_set_header Connection close; Context: http, server, location //扩展: proxy_hide_heade rproxy_set_body
5.代理理到后端的TCP连接超时
1 2 3 4 5 6 Syntax: proxy_connect_timeout time; Default: proxy_connect_timeout 60s; Context: http, server, location //扩展 proxy_read_timeout //以及建立 proxy_send_timeout //服务端请求完, 发送给客户端时间
6.Proxy常见配置项具体配置如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 [root@Nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/proxy_params proxy_redirect default; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_connect_timeout 30; proxy_send_timeout 60; proxy_read_timeout 60; proxy_buffer_size 32k; proxy_buffering on; proxy_buffers 4 128k; proxy_busy_buffers_size 256k; proxy_max_temp_file_size 256k; //具体location实现 location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; include proxy_params; }
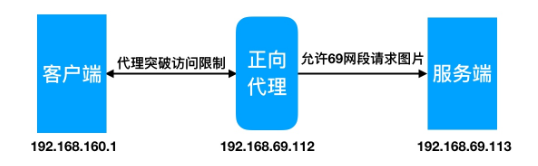
3 Nginx正向代理理示例
//配置69.113访问限制,仅允许同网段访问
1 2 3 4 5 location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ { allow 192.168.69.0/24; deny all; root /soft/code/images; }
//配置正向代理理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [root@Nginx ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/zy_proxy.conf server { listen 80; resolver 233.5.5.5; location / { proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } }
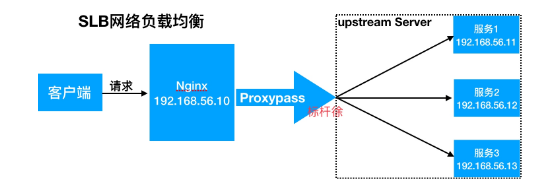
4 负载均衡 Nginx实现负载均衡用到了了proxy_pass代理理模块核心配置, 将客户端请求代理理转发至一组upstream虚拟服务池
Nginx upstream虚拟配置语法
1 2 3 Syntax: upstream name { ... } Default: - Context: http
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 //upstream例 upstream backend { server backend1.example.com weight=5; server backend2.example.com:8080; server unix:/tmp/backend3; server backup1.example.com:8080 backup; } server { location / { proxy_pass http://backend; } }
5 Nginx负载均衡状态配置 后端服务器在负载均衡调度中的状态
状态
概述
down
当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡
backup
预留的备份服务器
max_fails
允许请求失败的次数
fail_timeout
经过max_fails失败后, 服务暂停时间
max_conns
限制最⼤的接收连接数
配置示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 upstream load_pass { server 192.168.56.11:8001 down; server 192.168.56.12:8002 backup; server 192.168.56.13:8003 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=10s; } location / { proxy_pass http://load_pass; include proxy_params; }
6 Nginx负载均衡调度策略
调度算法
概述
轮询
按时间顺序逐⼀分配到不同的后端服务器(默认)
weight
加权轮询,weight值越⼤,分配到的访问⼏率越⾼
ip_hash
每个请求按访问IP的hash结果分配,这样来⾃同⼀IP的固定访问⼀个后端服务器
url_hash
按照访问URL的hash结果来分配请求,是每个URL定向到同个后端服务器
least_conn
最少链接数,那个机器链接数少就分发
hash关键数值
hash⾃定义的key
Nginx负载均衡权重轮询具体配置
1 2 3 4 5 upstream load_pass { server 192.168.56.11:8001; server 192.168.56.12:8002 weight=5; server 192.168.56.13:8003; }
Nginx负载均衡 ip_hash 具体配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 //如果客户端都相同代理, 会导致某台服务器连接过多 upstream load_pass { ip_hash; server 192.168.56.11:8001; server 192.168.56.12:8002; server 192.168.56.13:8003; }
Nginx负载均衡url_hash具体配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 //如果出现通过代理访问会影响后端节点接收状态均衡 upstream load_pass { hash $request_uri; server 192.168.56.11:8001; server 192.168.56.12:8002; server 192.168.56.13:8003; }